CT Scan for Lung Cancer: A Comprehensive Guide
Lung cancer remains one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths worldwide. Early detection is crucial, and one of the most effective methods for identifying lung cancer at an early stage is through a CT scan for lung cancer. This article aims to provide an in-depth understanding of CT scans, their advantages, and how they fit into modern lung cancer diagnosis.
What is a CT Scan?
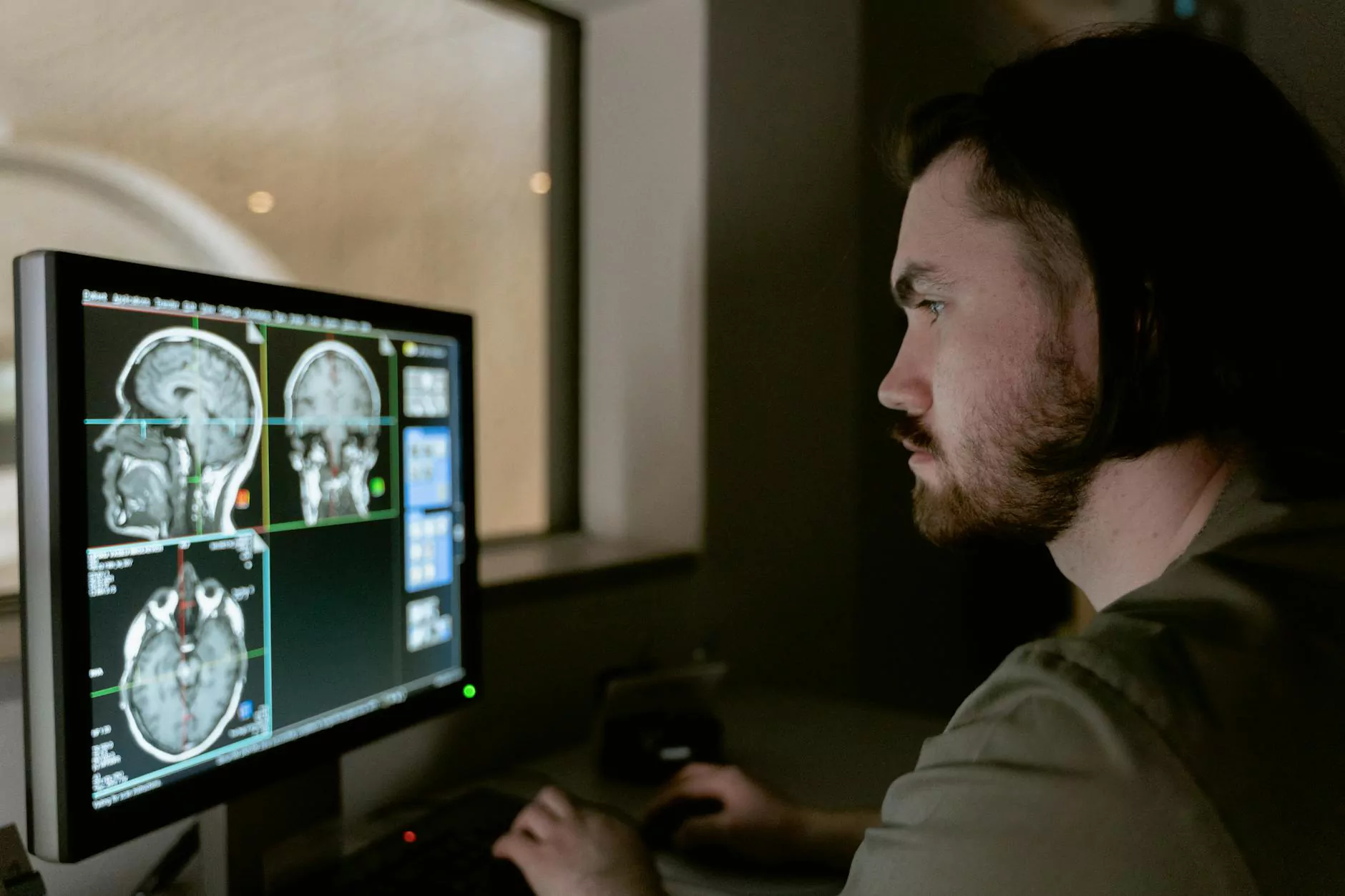
A Computed Tomography (CT) scan, also known as a CAT scan, is a sophisticated imaging technique that combines x-ray images taken from different angles and uses computer processing to create cross-sectional images of bones, blood vessels, and soft tissues inside the body. This technology provides more detailed information than traditional x-rays, making it a valuable tool in diagnosing various health conditions, including lung cancer.
Why a CT Scan is Vital in Lung Cancer Detection
Unlike many other forms of cancer, lung cancer can often develop silently, without presenting significant symptoms until it has progressed to later stages. A CT scan for lung cancer plays a crucial role for several reasons:
- Early Detection: CT scans can detect small nodules that may indicate the presence of cancer before symptoms appear.
- Detailed Imaging: Provides high-resolution images that help differentiate between benign and malignant nodules.
- Guidance for Biopsies: A CT scan can guide healthcare professionals in performing biopsies, where tissue samples are needed to confirm cancer.
- Monitoring Progress: For patients already diagnosed with lung cancer, CT scans are essential in monitoring tumor growth and response to treatment.
How CT Scans Work
A CT scan for lung cancer typically involves the following steps:
- Preparation: Patients are usually instructed to avoid food or drink for a few hours before the scan. They may also need to remove any metallic objects.
- Positioning: The patient lies on a table that slides into the CT scanner. They must remain still to ensure clear images are captured.
- Contrast Material: In some cases, a contrast dye may be administered to enhance the images and highlight specific areas of concern.
- Image Capture: The scanner rotates around the patient, taking multiple images which are then processed into cross-sectional slices of the lungs.
- Review: A radiologist reviews the images to identify any abnormalities, which is crucial for making a diagnosis.
Benefits of CT Scans in Lung Cancer Diagnosis
CT scans offer numerous advantages that make them indispensable in lung cancer detection:
1. High Sensitivity and Specificity
CT scans have been shown to have high sensitivity and specificity for detecting lung nodules, allowing for better early-stage identification of lung cancer.
2. Non-invasive and Quick
The procedure is relatively quick, typically lasting only a few minutes, and is non-invasive, making it a preferred choice for patients.
3. Risk Stratification
CT imaging helps in risk assessment by providing detailed information about the size, shape, and characteristics of lung nodules.
4. Versatile Utility
CT scans are useful not only for diagnosis but also for ongoing monitoring of lung cancer treatment and progression.
Preparing for a CT Scan
Proper preparation can enhance the quality of CT scans and ensure accurate results. Here are essential steps patients should consider:
- Consult with the healthcare provider regarding medication and dietary restrictions.
- Inform the medical staff about any allergies, especially to contrast material.
- Wear comfortable clothing that is free of metal embellishments.
- Discuss any concerns about anxiety or claustrophobia during the procedure.
Understanding CT Scan Results
Following a CT scan, the results are typically available within a few days. Here’s how to interpret the findings:
- Normal Results: No suspicious nodules are detected.
- Benign Findings: Some nodules may be present but are determined to be non-cancerous.
- Suspicious Findings: Nodules that have characteristics indicating a higher risk of malignancy may require further testing or biopsy.
CT Scans and Lung Cancer Screening
CT scans play a prominent role in lung cancer screening, especially for high-risk individuals, such as those with a significant smoking history. The following points summarize the significance:
- National Screening Guidelines: Organizations like the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommend annual low-dose CT scans for adults aged 50-80 with a history of heavy smoking.
- Early Treatment: Early detection through screening can lead to timely treatment options that significantly improve survival rates.
- Continued Research: Ongoing studies continue to evaluate the effectiveness of CT screening in reducing lung cancer mortality rates.
The Future of CT Scans in Lung Cancer Diagnosis
As technology advances, the capability of CT scans continues to improve. Innovations in imaging technologies, such as machine learning and artificial intelligence, are on the horizon, promising:
- Enhanced Accuracy: AI algorithms can analyze imaging data, improving the detection rate of lung cancer.
- Personalized Screening: Future iterations may focus on personalized screening strategies based on individual risk factors.
- Integrated Care: Combining CT imaging with other diagnostic modalities could lead to more comprehensive care approaches.
Conclusion
The CT scan for lung cancer has revolutionized the way we approach the diagnosis and management of lung cancer. Its ability to detect the disease early gives patients a better chance for successful treatment and improved outcomes. As advancements in technology continue to evolve, patients and healthcare providers alike can expect even greater enhancements in lung cancer detection and management. If you or a loved one is at risk, consult with a healthcare professional about the importance of regular screenings and the role of CT scans in catching lung cancer early.









